The power conversion efficiencies of organic solar cells (OSCs) based on blends of electron donor (D) and acceptor (A) semiconducting materials now exceed 16%. However, it is still lower than that of highly efficient inorganic SCs such as GaAs. The charge generation efficiency in OSCs nowadays is nearly 100%, thus reducing the energy loss in output voltage is critically important for further enhancing the efficiency of organic solar cells.
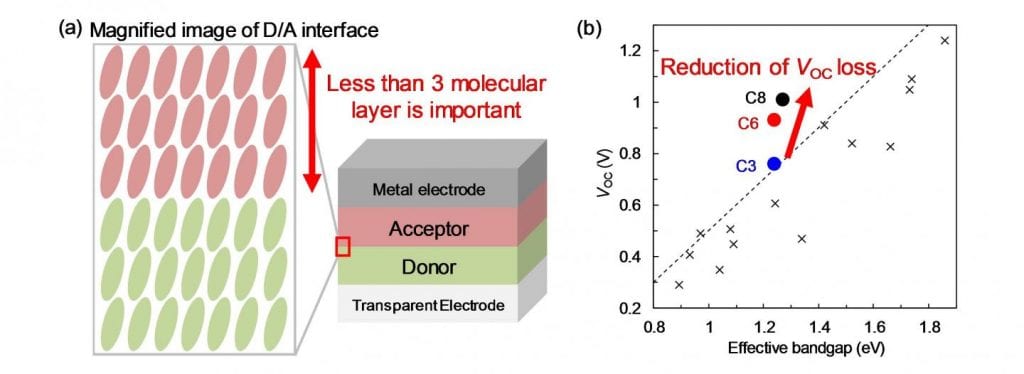
Assistant Professor Seiichiro Izawa and Professor Masahiro Hiramoto at Institute for Molecular Science in Japan reported that OSCs with high mobility and highly crystalline donor (D) and acceptor (A) materials were able to reduce an open-circuit voltage (VOC) loss. Researchers fabricated model bilayer OSCs using these molecules (Fig. 1a). The crystallinity of the acceptor layer could be altered by appropriate selection of the three molecules with different alkyl side-chain lengths. The VOC was found to increase as the crystallinity of acceptor layer increased. The VOC loss was very small comparing to the values of reported OSCs (Fig 1b). The origin of the high VOC was that the highly crystalline D/A interface reduced the energy loss related to charge recombination in the output voltage by realizing ideal band-to-band recombination. Especially, the high crystallinity of the several molecular layers (less than 6 nm) in the vicinity of the D/A interface was important for realizing the high VOC. The results demonstrate that careful design of the D/A interface enables high power conversion efficiencies to be achieved in OSCs by reducing open-circuit voltage loss.