Everspin Technologies, Inc.‘s (NASDAQ: MRAM) partner Cobham Advanced Electronic Solutions (CAES) recently presented a technical case study describing the versatility and performance of their jointly developed Toggle MRAM for space applications.
Nordson Corporation Announces Business Realignment and Leadership Appointments
Nordson Corporation (Nasdaq: NDSN) today announced a strategic business realignment that will position the company for its next chapter of profitable growth. The company will reorganize into two businesses: Industrial Precision Solutions (IPS) led by Gregory P. Merk, Executive Vice President, and Advanced Technology Solutions (ATS) led by Jeffrey A. Pembroke, Executive Vice President.
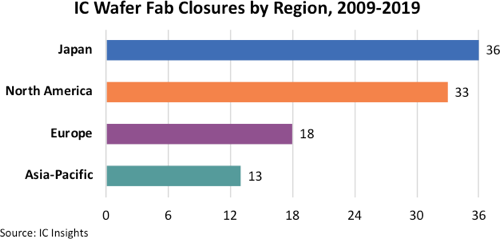
100 IC Wafer Fabs Closed or Repurposed Since 2009
Hardest hit are ≤200mm wafer fabs; 70% of closures in Japan and North America.
Toshiba’s 80V N-channel Power MOSFETs Fabricated with Latest Generation Process Help Improve Power Supply Efficiency
Toshiba Electronic Devices & Storage Corporation (“Toshiba”) has added 80V N-channel power MOSFETs to its “U-MOS X-H series” fabricated with the latest generation process. The new MOSFETs are suitable for switching power supplies in industrial equipment used in data centers and communication base stations.
Scientists Model Conditions of Ischemia on a Microfluidic Device
Researchers led by biomedical engineers at Tufts University invented a microfluidic chip containing cardiac cells that is capable of mimicking hypoxic conditions following a heart attack – specifically when an artery is blocked in the heart and then unblocked after treatment. The chip contains multiplexed arrays of electronic sensors placed outside and inside the cells that can detect the rise and fall of voltage across individual cell membranes, as well as voltage waves moving across the cell layer, which cause the cells to beat in unison in the chip, just as they do in the heart.
Double-Walled Nanotubes Have Electro-Optical Advantages
One nanotube could be great for electronics applications, but there’s new evidence that two could be tops. Rice University engineers already knew that size matters when using single-walled carbon nanotubes for their electrical properties. But until now, nobody had studied how electrons act when confronted with the Russian doll-like structure of multiwalled tubes.
ON Semiconductor Names Digi-Key Electronics Global High Service Distributor of the Year
Digi-Key Electronics, the leading global electronic components distributor, was named ON Semiconductor’s Global High Service Distributor for 2019. The Top 2019 High Service Distribution Partner Award honors the distributor that led the channel in digital marketing initiatives, increased customer breadth, and promotion and sales of ON Semiconductor’s latest innovative new products. Digi-Key was recognized for partnering in inventory management and scoring highly on overall process excellence in the evolving semiconductor market.
Worldwide Server and Enterprise Storage Systems Markets Will Decline in 2020, Impacted by the COVID-19 Pandemic, According to IDC
End user spending on IT infrastructure (server and enterprise storage systems) will decline in 2020 as a result of the widespread coronavirus pandemic. According to the International Data Corporation (IDC) Worldwide Quarterly Server Tracker and Worldwide Quarterly Enterprise Storage Systems Tracker, under the current probable scenario server market revenues will decline 3.4% year over year to $88.6 billion and external enterprise storage systems (ESS) revenues will decline 5.5% to $28.7 billion in 2020.
New Fabrication Approach Paves Way to Low Cost Mid-Infrared Lasers Useful for Sensing
For the first time, researchers have fabricated high-performance mid-infrared laser diodes directly on microelectronics-compatible silicon substrates. The new lasers could enable the widespread development of low-cost sensors for real-time, accurate environmental sensing for applications such as air pollution monitoring, food safety analysis, and detecting leaks in pipes.
Juniper Research: Coronavirus to Cause $42 Billion Revenue Gap in Global Consumer Device Shipments over the Next 9 Months
New analysis from Juniper Research found that Coronavirus could cause around a $42 billion revenue gap over the next 9 months for smart device vendors. The analysis examined a number of key device verticals including smartphones, tablets, consumer robotics, smart speakers and smart wearables. Three impact scenarios, low, medium and high, illustrate a range of possible outcomes.