ACM Research, Inc. (NASDAQ: ACMR), a leading supplier of wafer cleaning technologies for advanced semiconductor devices, today unveiled the Ultra Furnace, its first system developed for multiple dry processing applications.
Semiconductors
Mike Schuh Joins D2S Board of Directors
D2S, a supplier of GPU-accelerated solutions for semiconductor manufacturing, today announced the appointment of Mike Schuh to its board of directors, effective immediately. Mike has more than 40 years of experience in the software industry, including holding senior executive management and board-level roles at several electronic design automation (EDA) and technology companies, with more than 10 years of board-level experience at Netflix. “Mike has unparalleled experience in sales and corporate strategy across…
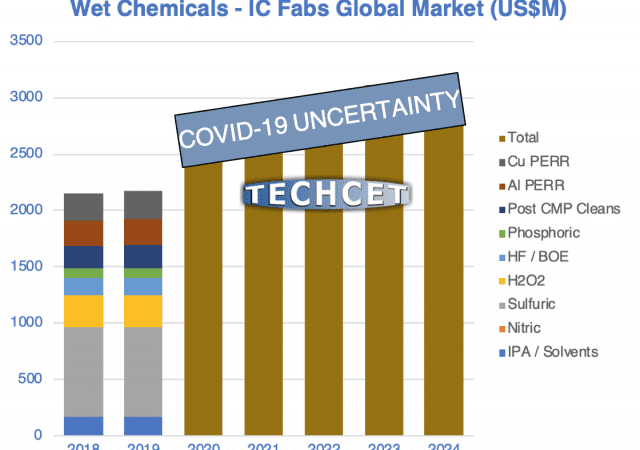
CMC Workshop Flags Looming Shortages of IPA and Sulfuric
These extraordinary times of greater risks call for more information, so the Critical Materials Council (CMC) of semiconductor fabricators & suppliers is now meeting briefly several times a month to exchange pre-competitive information to mitigate potential supply- chain disruptions.
GLOBALFOUNDRIES Dresden Certified to Manufacture Secure Products
The German Federal Office for Information Security (Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik, BSI) has certified the GLOBALFOUNDRIES® (GF®) Dresden site according to the latest international Common Criteria standard (ISO 15408, CC Version 3.1). In a “virtual ceremony”, the certificate was presented today to Dr. Thomas Morgenstern, SVP and General Manager of GF in Dresden, by Arne Schönbohm, President of the BSI and Minister Oliver Schenk, the head of the Saxony State Chancellery.
Despite COVID-19 Outbreak, Edge Computing to Drive Next Wave of Innovation in Asia-Pacific
Edge computing is poised to garner a lot of interest in Asia-Pacific, as emphasis on improving networking technologies for remote working grows amidst the current coronavirus (Covid-19) pandemic. The market for edge computing in APAC is estimated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21% between 2019 and 2024 to reach US$ 5.8bn in 2024, says GlobalData, a leading data and analytics company.
North American Semiconductor Equipment Industry Posts March 2020 Billings
North America-based manufacturers of semiconductor equipment posted $2.21 billion in billings worldwide in March 2020 (three-month…
NXP Supplies Murata with RF Front-end ICs for Wi-Fi 6 Modules
NXP Semiconductors N.V. (NASDAQ: NXPI) today announced it has collaborated with Murata, a system-in-package integrator for 5G mobile platforms, to deliver the industry’s first radio frequency (RF) front-end modules designed with the latest Wi-Fi 6 standards.
A New Way to Cool Down Electronic Devices, Recover Waste Heat
Using electronic devices for too long can cause them to overheat, which might slow them down, damage their components or even make them explode or catch fire. Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Nano Letters have developed a hydrogel that can both cool down electronics, such as cell phone batteries, and convert their waste heat into electricity.
Intel and QuTech Demonstrate High-Fidelity ‘Hot’ Qubits for Practical Quantum Systems
Intel Corporation has invented a spin qubit fabrication flow on its 300 mm process technology using isotopically pure wafers.
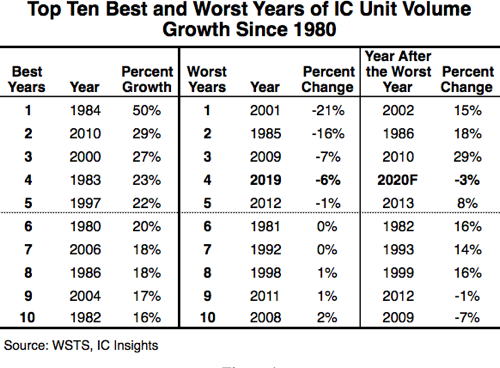
IC Unit Shipments Forecast to Display First-Ever Back-to-Back Decline
A rare decline in IC unit shipments in 2019 expected to be followed by another drop in 2020.